FOLLICULAR SCAN FOR OVULATION DURING IUI / IVF
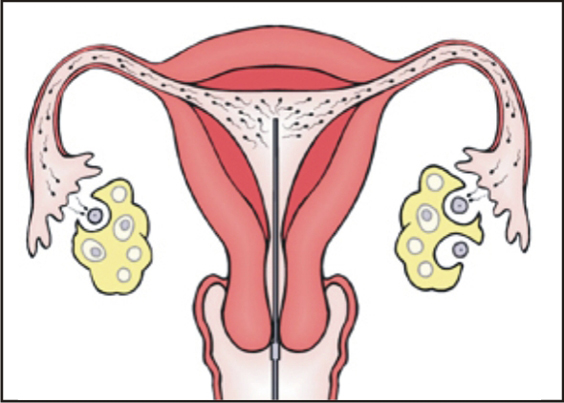
In a regular menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from a growing follicle in the ovary and pushed into the fallopian tube and is available to be fertilised.If no fertilisation happens then the unfertilised egg and the uterine lining is shed as menstruation.Ovulation usually happens 14 days prior to the next expected period.We can track the events of a growing follicle with ovulation happening through a regular menstrual cycle from day 9 to day 20 by repeated transvaginal scans known as FOLLICULOMETRY.
What are the stages of Follicular Scans?
1) BASELINE SCAN:-
This scan is done on day2 / day3 of a menstrual cycle which gives very vital information like:-
- Antral follicle count – which signifies the ovarian reserve(PCO/DOR)
- Simple cysts/Endometriosis cysts
- Fibroids
- Endometrial cavity assessment
2) SCAN ON DAY 9/10:-
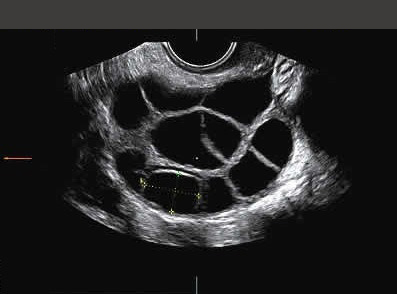
Subsequently the scan is done to check the growth of a follicle which is a thin walled structure containing fluid along with egg attached to the inner side of membrane. The follicle appears as a black bubble on the scan which grows at the rate of 1-2mm per day.
3) SCAN DONE AROUND DAY 11/DAY 13:-
This scan shows a dominant follicle of size about 17-25mm in diameter with good perivascular flow >90% and resistance index < 0.1. a good quality should have a good blood flow and optimum size which indicates good ovum.
Besides the dominant follicle, the endometrial thickness should also be 7-10mm with good vascularity. A 3D picture of the cavity can be constructed to exclude any indenting lesion like polyps or fibroid etc.
4) DAY 14-16 SCAN TO CHECK FOR OVULATION:-
The disappearance of the dominant follicle, and presence of irregular walled cystic structure on subsequent scans indicates ovulation. In addition there is some fluid present in the P.O.D which signifies ovulation.
Advantages of Folliculometry:-
- Follicles which do not grow till the optimum size before rupturing can be diagnosed – Premature rupture of follicles.
- Some follicles do not grow at all can be detected.
- Some dominant follicles do not rupture – Luteinized unruptured follicle.
- The endometrial lining not good enough in thickness or quality.
- To predict the time of ovulation – in assisted reproductive techniques.
- To guide treatments with ovulation inducing drugs or injections.
- To detect complications early like OHSS and treat early.
- To detect luteal phase deficiency.